Meme coins burst onto the crypto scene with wild energy and a blend of humor and high-risk speculation. They are designed to capture attention through viral internet culture, social media hype, and clever names. Many of these coins saw meteoric rises only to fall just as dramatically. In this article, we explore 10 popular meme coins that never recovered. We review their beginnings, analyze their tokenomics, and examine the key factors that led to their decline. Our goal is to provide a clear and professional analysis, drawing lessons for both new and seasoned investors. By understanding the pitfalls of these projects, you can learn valuable strategies for evaluating emerging coins in the crypto space.
Top 10 Meme coins that never recovered
- SafeMoon
- Hoge Finance
- CumRocket
- ElonDoge
- Saitama Inu
- MoonMoon
- Pitbull Token
- FEG Token
- Kishu Inu
- Akita Inu
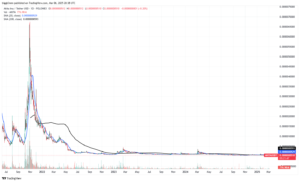
SafeMoon
SafeMoon emerged in early 2021 and quickly became one of the most well-known meme coins. The project caught the public’s attention with its unique tokenomics. SafeMoon introduced a model where every transaction incurred a fee, part of which was redistributed to existing holders while another portion was burned. This structure was designed to reward long-term holding and create a deflationary supply. The coin’s launch was accompanied by significant community engagement and robust social media campaigns, which helped drive up its initial market value.
The coin’s branding was simple yet memorable, combining elements of safety and community-driven finance. It was marketed as a revolutionary asset that could protect investors from market volatility while generating passive rewards. The tokenomics and innovative fee structure attracted a large number of investors, many of whom hoped to reap huge rewards. Despite the initial enthusiasm, the promise of SafeMoon was largely built on hype rather than a fully developed technical roadmap. Many investors were drawn to the idea of exponential gains, only to discover that the underlying model had serious limitations.
Why SafeMoon Failed
SafeMoon’s downfall can be attributed to several interlinked factors. First, its tokenomics proved to be unsustainable over the long term. The high transaction fees, intended to reward holders, also discouraged active trading. This led to a lack of liquidity, as few new buyers entered the market. When liquidity dries up, price discovery suffers, and investor confidence declines.
Moreover, the high fee structure created an environment where even genuine users found it difficult to transact without incurring significant costs. This issue was compounded by the fact that there was little tangible utility for the token beyond speculative gains. Investors started to question the long-term viability of a coin that offered no clear use case or development roadmap. The rapid rise in popularity turned into a double-edged sword as expectations soared but were never met.
Another reason behind SafeMoon’s decline was the increasing regulatory scrutiny of such projects. As governments and financial institutions began to examine the crypto market more closely, projects that lacked robust legal frameworks and clear use cases came under fire. The community’s trust in SafeMoon waned as the initial promise of a decentralized, community-driven asset was overshadowed by mounting concerns over transparency and sustainability.
Hoge Finance
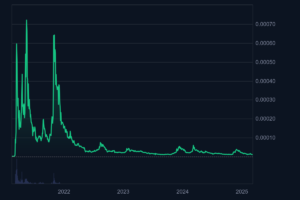
Hoge Finance entered the crypto market with a mission to mix the fun of meme culture with innovative tokenomics. It was launched as a community-driven project that promised to reward its loyal supporters. Similar to other meme coins, Hoge Finance was built around an attractive narrative and a decentralized approach. The coin leveraged social media to rapidly gain traction, tapping into the enthusiasm of a vibrant online community.
The project was initially celebrated for its bold promises and playful branding. Hoge Finance aimed to differentiate itself by combining deflationary mechanics with a charitable component, where a portion of every transaction fee was allocated to charity. This combination of financial incentives and social good resonated with many investors who were looking for projects with a positive impact.
Why Hoge Finance Failed
Despite its promising start, Hoge Finance encountered multiple challenges that led to its decline. One significant issue was low liquidity. In the crypto market, liquidity is critical for price stability and market confidence. Hoge Finance struggled to maintain consistent trading volumes, which made it vulnerable to price manipulation and volatility. The low liquidity made it difficult for investors to enter or exit positions without causing large price swings.
Additionally, Hoge Finance suffered from poor governance. The decentralized nature of the project, while appealing in theory, meant that decision-making was often slow and fragmented. Promised innovations were delayed, and key strategic decisions were not executed as planned. The lack of a clear and cohesive roadmap eroded investor trust, which is crucial in a market as competitive and fast-moving as crypto.
The combination of low liquidity and ineffective governance led to a situation where even loyal community members began to lose confidence. As the project failed to deliver on its promises, the initial enthusiasm dwindled, and many investors started to sell off their holdings. The decline in market confidence accelerated the downward spiral, causing the value of Hoge Finance to drop significantly.
CumRocket
CumRocket was one of the more controversial meme coins, carving out a niche in the adult content industry. It quickly gained attention due to its provocative name and the promise of a specialized platform that would bring cryptocurrency to the world of adult entertainment. The coin’s launch was marked by a surge in social media buzz and viral marketing tactics. CumRocket aimed to provide a safe and efficient payment system for adult content creators and their fans.
The project’s niche focus was seen as both a strength and a potential risk. On one hand, it promised to tap into a large and underbanked segment of the digital economy. On the other hand, its association with adult content meant it would face additional regulatory scrutiny and reputational challenges. Nonetheless, the initial buzz was enough to drive significant investment and market activity, at least in the short term.
Why CumRocket Failed
CumRocket’s failure can be linked to several critical issues. Foremost among them were regulatory hurdles. The adult content industry is heavily regulated in many jurisdictions, and the integration of cryptocurrency into this space only amplified those concerns. Regulatory bodies were wary of a coin that could potentially facilitate transactions in a highly scrutinized industry. As a result, CumRocket found itself facing legal uncertainties that hindered its broader adoption.
Moreover, CumRocket struggled to gain mainstream adoption. While the coin initially garnered attention for its bold and unconventional approach, it lacked the utility and broad appeal necessary to sustain long-term interest. The niche market that it targeted proved to be too limited to support the high levels of investment needed for significant growth. Investors began to realize that the coin’s business model was not scalable, and its initial viral success was not backed by a viable long-term strategy.
Reputational challenges also played a significant role in the decline of CumRocket. The name itself, while catchy, created barriers to acceptance in more conservative markets and among institutional investors. The project’s focus on adult content made it difficult to form partnerships with mainstream platforms or financial institutions. Over time, the negative connotations associated with the coin overshadowed its early promise, leading to a rapid decline in investor confidence and market value.
ElonDoge
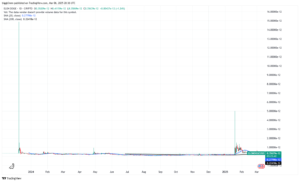
ElonDoge entered the market riding on the coattails of two of the most recognizable names in the meme world: Elon Musk and Dogecoin. The project leveraged the popularity of these icons to create a buzz that was hard to ignore. ElonDoge was designed to be fun, energetic, and reflective of the exuberance found in many meme coin projects. The coin quickly gained traction due to its clever name and the association with the larger-than-life persona of Elon Musk, who has often been a topic of discussion in the crypto community.
The project promised to combine the viral nature of meme coins with a community-first approach. Its launch was marked by aggressive social media campaigns and endorsements by influential figures in the crypto space. For a time, ElonDoge enjoyed a surge in market activity, buoyed by investor speculation and the lure of potentially explosive returns.
Why ElonDoge Failed
ElonDoge’s decline is a classic case of overreliance on hype without substance. The coin was heavily dependent on the buzz generated by its association with popular memes and high-profile figures. However, this reliance on external hype meant that when the excitement faded, so did the investor interest. The lack of a clear and practical use case made it difficult for the coin to sustain momentum.
A key issue was the rapid dilution of investor interest. As more meme coins entered the market, ElonDoge was quickly overshadowed by newer projects that promised innovative features or more robust tokenomics. The market became saturated with similar coins, and the unique selling point of ElonDoge was lost in the noise. Additionally, the project lacked a solid roadmap or development milestones, which further diminished investor confidence.
The absence of tangible utility for ElonDoge contributed significantly to its downfall. Investors are increasingly looking for projects that offer more than just speculative gains. Without real-world applications or meaningful partnerships, ElonDoge was unable to justify its initial valuation. Over time, the coin’s value eroded as more savvy investors moved on to projects with stronger fundamentals and clearer paths to sustainability.
Saitama Inu
Saitama Inu was another meme coin that captured the imagination of investors with its community-driven marketing strategies and ambitious promises. Named after a popular fictional character, the coin aimed to create a vibrant ecosystem that went beyond simple speculation. The team behind Saitama Inu positioned the project as one that would educate and empower its community, with promises of financial freedom and innovative technology integrations.
The project built a large and active community, leveraging social media, influencer endorsements, and targeted advertising. Saitama Inu’s marketing efforts were relentless, and its messaging was crafted to resonate with a wide audience. Investors were attracted by the notion of being part of a movement rather than just a financial asset, and the coin enjoyed rapid price increases during its initial phases.
Why Saitama Inu Failed
Despite its strong community focus and bold promises, Saitama Inu struggled to deliver on its high expectations. One of the main reasons for its failure was the inability to meet development milestones. Promised technological innovations and ecosystem expansions were repeatedly delayed or scaled back. This led to growing frustration among investors who had hoped for a revolutionary platform that would disrupt traditional finance.
Another factor was the market’s saturation with similar projects. As more meme coins entered the space, investors began to question the uniqueness of Saitama Inu. The coin’s value proposition was diluted in a market flooded with competitors offering comparable community engagement and speculative returns. With too many similar projects vying for attention, Saitama Inu found it increasingly difficult to stand out.
Moreover, the ambitious vision of the project was not backed by sufficient technical expertise or financial resources. Without a clear plan for sustainable growth, Saitama Inu’s community was left with a promise that could not be fulfilled. The resulting disappointment led to a significant sell-off, as investors lost faith in the project’s ability to deliver real value over time.
In essence, Saitama Inu’s failure highlights the dangers of overpromising without adequate follow-through. A strong community and engaging marketing cannot substitute for a clear, achievable roadmap and the technical capabilities needed to bring a project to life.
MoonMoon
MoonMoon was launched at a time when meme coins were the talk of the crypto world. It capitalized on the catchy, playful nature of its name and the promise of a fun, engaging investment opportunity. The project attracted a substantial following thanks to its vibrant social media presence and enthusiastic community. MoonMoon was marketed as a coin that would take investors “to the moon,” a common phrase in the crypto lexicon that signifies rapid gains and high aspirations.
The team behind MoonMoon relied on creative branding and viral marketing tactics to generate interest. The initial excitement was palpable, with many early adopters expressing hope that the coin would revolutionize the meme coin space. Investors were drawn to the playful yet ambitious messaging, which promised both entertainment and financial rewards.
Why MoonMoon Failed
MoonMoon ultimately failed to live up to its lofty promises. A primary reason for its decline was the project’s inability to sustain interest beyond the initial hype phase. The coin’s underlying fundamentals were weak, and its value was driven almost entirely by social media buzz rather than solid technical or economic fundamentals.
Lack of real-world applications further contributed to MoonMoon’s downfall. Without a clear utility or roadmap for developing meaningful features, the coin was unable to retain investor interest as market conditions shifted. The project’s management also struggled with transparency and effective communication, leading to doubts about the coin’s long-term viability.
The management team’s inability to address these challenges in a timely manner resulted in a rapid decline in investor confidence. As the hype dissipated, so did the coin’s market value. MoonMoon serves as a clear example of a project that relied too heavily on catchy marketing and viral trends without backing up its promises with solid, actionable plans.
Pitbull Token
Pitbull Token was launched with an aggressive marketing strategy and a promise of rapid gains. The project aimed to leverage celebrity endorsements and bold promotional tactics to build a strong brand image. Pitbull Token was designed to appeal to a wide audience, from crypto enthusiasts to casual investors who were drawn by the glitz of celebrity influence and the excitement of a trending meme coin.
The project’s creators positioned Pitbull Token as a coin with a strong and resilient community. The aggressive marketing campaigns, combined with high-profile endorsements, generated significant media attention. For a time, Pitbull Token was seen as a promising addition to the meme coin universe, with investors betting on its ability to disrupt the market and deliver unprecedented returns.
Why Pitbull Token Failed
Pitbull Token’s failure can largely be attributed to overhype and regulatory concerns. The coin was marketed with bold promises that were not backed by a sound business model. The aggressive tactics used in its promotion led to inflated expectations that could not be met in the long run. When the promised returns and innovations failed to materialize, investor sentiment turned sharply negative.
Regulatory scrutiny was another major issue. As financial authorities began to examine the practices of cryptocurrency projects more closely, Pitbull Token’s aggressive marketing and lack of substantive development attracted unwanted attention. Investors grew wary of potential legal implications, and the mounting regulatory concerns contributed significantly to the token’s decline.
Additionally, the project suffered from a lack of transparency. As details about the team and their long-term plans remained vague, confidence in the coin’s future waned. The combination of overhyped marketing, regulatory red flags, and an opaque governance structure ultimately led to a rapid drop in value, leaving many investors with significant losses.
FEG Token
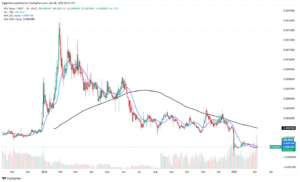
FEG Token was introduced as a deflationary asset with a promise of rewarding long-term holders. The token’s design was centered on a unique fee structure that redistributed a portion of each transaction back to its community, while simultaneously burning a fraction of the supply to create a deflationary effect. This model was intended to encourage holding and reduce overall supply over time, theoretically increasing the token’s value.
The initial launch of FEG Token was met with enthusiasm by crypto enthusiasts who were intrigued by the deflationary model. The token was marketed as a revolutionary asset that combined innovative tokenomics with community rewards. Early investors were attracted by the promise of steady, passive income through token redistribution, and the coin quickly gained traction on various social media platforms.
Why FEG Token Failed
Despite its innovative approach, FEG Token struggled to maintain a sustainable growth model. One of the critical issues was inconsistent development. Although the tokenomics were designed to reward holders, the project failed to deliver on continuous innovation and improvements in its ecosystem. This led to growing doubts among investors about the long-term viability of the project.
Market manipulation also emerged as a significant concern. In an environment where speculative trading is rampant, FEG Token became a target for pump-and-dump schemes and other forms of market manipulation. These practices created an unstable market environment that undermined the deflationary model. As trust in the project diminished, investor confidence waned, leading to a sustained decline in market value.
Furthermore, the economic model of FEG Token, while initially appealing, did not prove to be scalable in the face of real market dynamics. Without a clear pathway to integrate its tokenomics with real-world use cases or a robust development roadmap, the coin was unable to adapt to changing market conditions. The failure to address these challenges ultimately led to its inability to recover from early setbacks.
Kishu Inu
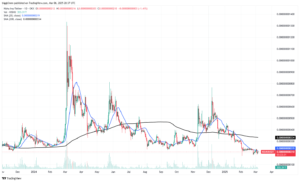
Kishu Inu was one of the meme coins that experienced rapid growth, driven largely by social media trends and influencer endorsements. The coin was modeled after other popular “dog coins” and sought to capitalize on the viral nature of cute animal imagery and community-driven promotions. Kishu Inu’s marketing strategy focused on building a massive online following, with its developers actively engaging in social media campaigns and community events.
At its peak, Kishu Inu was seen as a promising project that combined fun branding with the potential for explosive gains. The coin attracted a diverse group of investors, from seasoned crypto traders to newcomers lured by the promise of quick profits. Its rapid rise in value was fueled by an aggressive marketing strategy and the natural appeal of its brand imagery.
Why Kishu Inu Failed
Kishu Inu ultimately fell victim to the inherent pitfalls of meme-based hype. While the coin’s social media presence was initially a strength, it also became a liability. The reliance on viral trends meant that Kishu Inu’s value was highly dependent on continuous hype rather than sound fundamentals. When the novelty wore off, investor interest began to wane, leading to a steep decline in market value.
A lack of innovative features further contributed to the coin’s downfall. Unlike projects that evolve by integrating new functionalities or real-world applications, Kishu Inu remained largely static. The absence of a clear developmental roadmap and tangible improvements meant that the coin could not differentiate itself in an increasingly crowded market. Investors eventually recognized that the project was built more on fleeting trends than on a foundation that could support long-term growth.
Market saturation also played a role in Kishu Inu’s failure. As more meme coins emerged with similar branding and tokenomics, the competition intensified. The oversaturation of the “dog coin” market left little room for differentiation, and many investors moved on to projects that offered unique value propositions. In the end, Kishu Inu’s initial momentum was not enough to overcome the fundamental issues that plagued its long-term prospects.
Akita Inu
Akita Inu was launched as another contender in the “dog coin” category. Drawing inspiration from its counterparts, the project aimed to create a community-centric ecosystem supported by active social media engagement and innovative tokenomics. Akita Inu quickly gained attention from investors who saw potential in its playful branding and the promise of a decentralized, community-driven asset.
The coin’s early days were marked by a surge in social media activity and enthusiastic support from crypto influencers. Investors were attracted to the idea of a coin that not only promised financial gains but also fostered a strong sense of community. Akita Inu was marketed as a coin with heart—a project that combined the fun of meme culture with the potential for rewarding long-term holding.
Why Akita Inu Failed
Despite the initial excitement, Akita Inu was unable to carve out a sustainable niche in the highly competitive meme coin market. One of the primary reasons for its decline was market saturation. The “dog coin” category became crowded with numerous similar projects, each vying for the attention of the same pool of investors. As a result, Akita Inu’s unique selling points were quickly diluted by the overwhelming number of alternatives.
The project also suffered from a limited vision and poor long-term planning. While early promotional efforts were robust, the development team failed to articulate a clear roadmap for integrating the token into practical use cases. Without ongoing innovation or concrete plans for expanding its ecosystem, investor enthusiasm gradually diminished. The project’s inability to differentiate itself from other meme coins led to a steady erosion of its market value.
Furthermore, dwindling community support compounded the issues. In the volatile crypto environment, sustained community engagement is crucial. As investor interest waned, key community members started to lose faith, leading to a downward spiral in both trading volume and overall market confidence. Akita Inu’s experience is a reminder that even well-branded projects must back their hype with real utility and a forward-thinking development strategy.
How To Spot A Failing Crypto Project
After reviewing these case studies, it is important to highlight key strategies that can help you identify warning signs in any crypto project. The following tips are designed to assist you in making more informed decisions and avoiding pitfalls similar to those experienced by many meme coins.
Evaluate Tokenomics and Supply Structure
The structure of a coin’s tokenomics can reveal a great deal about its long-term sustainability. Look for projects that have a balanced approach to token distribution. Key factors to consider include:
- Transaction Fees: Excessively high fees can deter trading and limit liquidity.
- Redistribution Models: While rewarding holders is positive, overly complex redistribution mechanisms can lead to unsustainable economics.
- Burn Mechanisms: A deflationary model is attractive only if it is balanced and does not restrict market activity.
A healthy tokenomics structure should encourage long-term holding while still enabling sufficient liquidity and market participation. Evaluate whether the project’s tokenomics are built to support growth or if they might lead to issues such as market stagnation.
Assess the Development Roadmap and Milestones
A clear and achievable development roadmap is essential for any crypto project. Look for evidence that the team has met its previous milestones. Consider these points:
- Transparency: The team should communicate their progress regularly and openly.
- Realistic Goals: Ambitious promises are less important than realistic, achievable objectives.
- Technical Expertise: Evaluate whether the team has the background and skills to deliver on its promises.
Projects that fail to meet their stated milestones or provide vague future plans are often at higher risk of underperformance.
Monitor Trading Volume and Liquidity
Trading volume and liquidity are important indicators of a coin’s health. A project with declining volume can signal a loss of investor confidence. Keep an eye on:
- Volume Trends: Consistent or growing trading volumes are generally positive indicators.
- Market Depth: Sufficient liquidity is necessary to avoid drastic price fluctuations during large trades.
- Exchange Listings: Being listed on multiple, reputable exchanges can help ensure that there is enough liquidity to support trading.
Low or declining liquidity may indicate that investors are losing interest, which is a red flag for potential failure.
Scrutinize Community Engagement and Transparency
A vibrant, engaged community can be a sign of a healthy project. However, an overly hyped community with little substantive communication from the team can be misleading. Consider the following:
- Regular Updates: Projects should offer regular, transparent updates about their progress and challenges.
- Community Feedback: An active community that is engaged in meaningful discussion about the project’s future is a good sign.
- Social Media Trends: Look beyond the hype and see if there is substantial discussion on platforms such as Telegram, Discord, or Twitter that indicates real investor interest and confidence.
A declining or overly speculative community often signals deeper issues with the project’s fundamentals.
Analyze Market Position and Competitor Landscape
Understanding a project’s position in the broader market is crucial. Ask yourself:
- Unique Value Proposition: Does the project offer something new or better than its competitors?
- Market Saturation: Is the project entering a crowded market, or does it have a niche that is underexplored?
- Partnerships and Integrations: Look for evidence of strategic partnerships or integrations that add real value to the project.
A project that fails to carve out a unique niche or that is lost among a sea of similar meme coins is at high risk of failure, as seen in many cases discussed above.
Final Thoughts
The rise and fall of meme coins offer a microcosm of the broader challenges in the cryptocurrency market. They highlight the tension between the allure of rapid wealth and the necessity for thoughtful, long-term planning. By studying the failures of projects like SafeMoon, Hoge Finance, CumRocket, ElonDoge, Saitama Inu, MoonMoon, Pitbull Token, FEG Token, Kishu Inu, and Akita Inu, investors can gain a deeper understanding of what drives sustainable success in crypto.
The lessons from these projects are clear: sound tokenomics, robust liquidity, clear developmental milestones, and genuine community engagement are indispensable. Without these pillars, even the most promising meme coin is doomed to fade away. As the crypto landscape continues to expand and mature, these insights will be invaluable for both new entrants and experienced investors alike.
Investors should remain vigilant and conduct thorough due diligence before investing in any project. Remember that while meme coins can offer excitement and potential quick returns, the risks are equally high. In a space where volatility is the norm, a disciplined, research-based approach is essential for long-term success.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Always conduct your own research and consult with a qualified professional before making any investment decisions.